PACKMAN has two types of lists:
- Reference
- Drop-down
Parts of the Lists Page #
Lists pages have the following specific parts:
- List selector
- List details
- List table
List Selector #
The list selector shows all lists for the module you are in. When you choose a list from the Type box, the list details and list table display information that is relevant to the selected list.
List Details #
Shows the full details of the record selected in the List table.
List Table #
The list table displays all records of the list that is selected in the Type box. You can use the mouse or keyboard to browse the contents of the list table. Full details of the highlighted record are shown in the list details area.
Using the Lists Page #
Use the Lists page to:
- Add a new record
- Edit an existing record
- Delete a record
Adding a Record #
- From the Options menu, choose Module Setup.
The PACKMAN Setup screen is displayed. - Select the Lists tab.
- Choose the list required from the Type box.
- Choose New, then type in the details for the new record.
- Choose Save.
The list table is updated to show the new record.
Editing a Record #
- From the Options menu, choose Module Setup.
The PACKMAN Setup screen is displayed. - Select the Lists tab.
- Choose the list required from the Type box.
- Select the record from the list table and change its details.
- Choose Save.
Deleting a Record #
- From the Options menu, choose Module Setup.
The PACKMAN Setup screen is displayed. - Select the Lists tab.
- Choose the list from the Type box.
- Select the record from the list table, then choose Delete.
The record is deleted and the list table is updated.
Reference Lists #
PACKMAN includes the following lists for your reference:
- CALs
- Container Types
- HIC Reconciliation Codes
- Languages
- PDL Warnings
- Routes of Administration.
To access these lists:
- Choose Module Setup from the Options menu.
- Select the List tab.
- Choose the required list from the drop-down box.

As these are reference lists and are updated by Amfac, you can not change or edit them.
Drop-Down Lists #
Many of the entry boxes in PACKMAN (and other Amfac modules) have drop-down lists. These lists are set up and maintained on the Lists page of the PACKMAN Setup screen.
To open the Lists Setup screen:
- Choose Module Setup from the Options menu, then select the List tab.
Choosing the Add button at the bottom of any drop-down list in the work area will also take you to the Lists page for that particular list type.
Lists are especially useful for reporting and data management. You can report on sets of related data using the groupings in each list. Lists also help to limit the number of key strokes required to complete a task.
PACKMAN Lists #
PACKMAN has the following drop-down lists that can be edited:
- Address Types
- Doctor Types
- Drug Forms
- Health Funds
- Patient Types
- Phone Types
- Postcode
- Sig Definitions
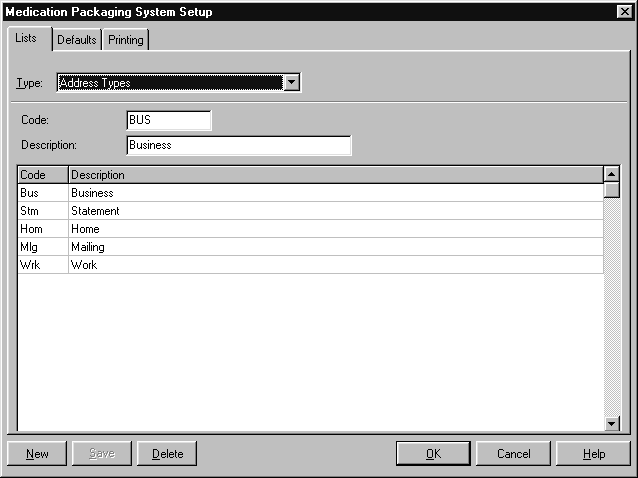
Address Types #
Amfac modules include commonly used address types. For example:
- Business
- Home
- Mailing
- Statement
- Work
To open the Address Types list:
- From the Options menu, choose Module Setup.
The PACKMAN Setup screen is displayed. - Select the Lists tab.
- Choose Address Types from the Type box.

To add a new address type when entering an address in the PACKMAN work area, type its description into the box at the top of the address area.
The following information is stored about each address type:
- Code
- Description
Doctor Types #
Amfac modules include a variety of different doctor types. These are useful for data management.
To open the Doctor list:
- From the Options menu, choose Module Setup.
The PACKMAN Setup screen is displayed. - Select the Lists tab.
- Choose Doctor from the Type box.
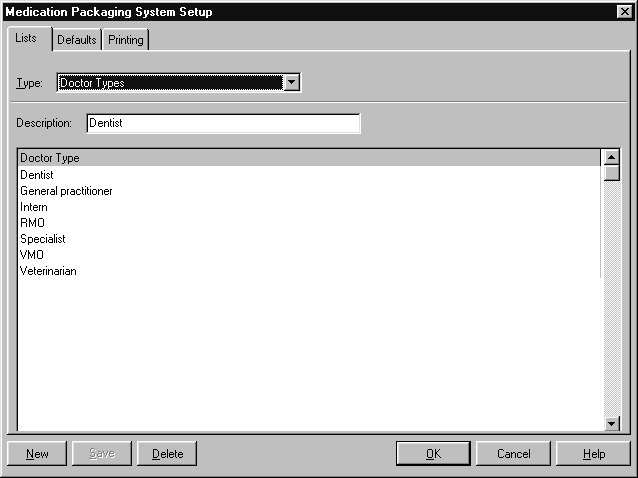
Amfac modules include the following commonly used doctor types:
- Dentist
- General Practitioner
- Intern
- RMO
- Specialist
- VMO
- Veterinarian
You can add new doctor types, or change the existing ones. A descriptive name for each doctor type is stored.
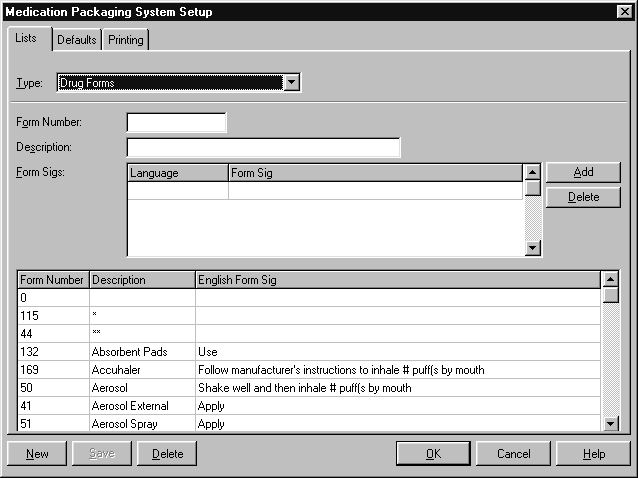
Drug Forms #
Amfac modules include a full set of drug form details. These are kept up to date as part of a regular drug update.
To open the Drug Forms list:
- From the Options menu, choose Module Setup.
The PACKMAN Setup screen is displayed. - Select the Lists tab.
- Choose Drug Forms from the Type box.
The following information is stored about each drug form:
- Amfac Form Number
- Description
- Form Sigs in various languages.
Form sigs describe how the drug form is administered. The software uses the form sigs to expand the ordinary sigs (entered by the user) to generate prescription directions specific to the drug form.
Form Sig Symbols
The following table lists the symbols used in the form sig expansions, and their meaning.
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| # | Dose quantity e.g. Take # tablet(s. |
| (s | For plural dose quantities add an s.e.g. Take # mL(s. |
| (ies | For plural dose quantities add an ies.e.g. Insert # suppository(ies in rectum. |
| (sful | For plural dose quantities add an sful.e.g. Disperse # teaspoon(sful in water. |
| e! | Replaced when dispensing by either each(e), both(b), left(l) or right(r).See Note below.e.g. Spray # puffs into e! nostrils. |

Some drug forms, such as ear and eye drops, require you to specify in the dosage directions whether the dose is for the left, right, both or each eye, ear, nose, etc.
For example:
With eye drops, the sig 1e bd expands to:Instil one drop in each eye twice a day
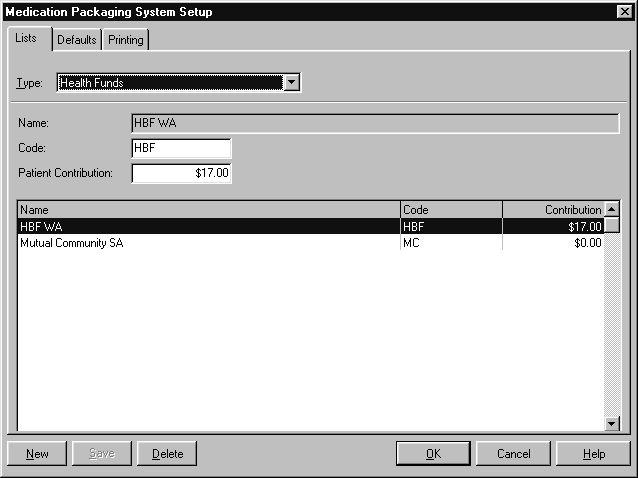
Health Funds #
Medication codes from several health funds are included in the regular data updates.
Use the Health Funds list to add new health funds, or set identifying codes and patient contributions for existing health funds.
The following information is stored about each health fund:
- Name
- Code
- Patient Contribution.
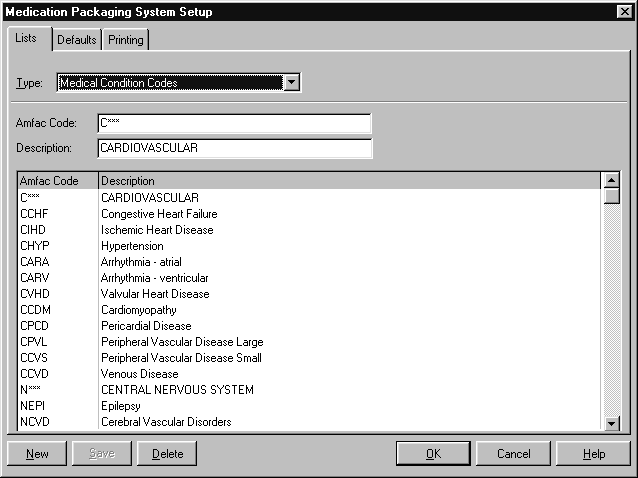
Medical Condition Codes
Amfac modules include a list of medical condition codes. In Healthlinks Dispensing, these codes are used to check the suitability of medications for patients.
To open the Medical Condition Code list:
- From the Options menu, choose Module Setup.
The PACKMAN Setup screen is displayed. - Select the Lists tab.
- Choose Condition Codes from the Type box.
The following information is stored about each medical condition:
- Code
- Description

PACKMAN does not currently screen for contra-indications between conditions entered for the patient and the drugs entered in their profile as this is done by dispensing software.
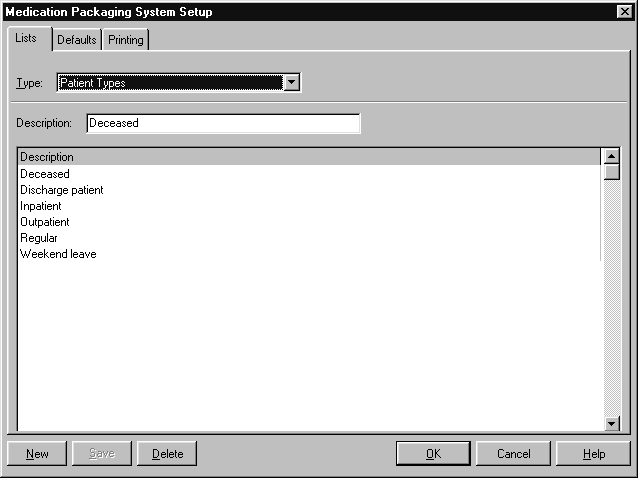
Patient Types #
Amfac modules include a variety of patient types. Patient types are useful for reporting and data management.
To open the Patient Types list:
- From the Options menu, choose Module Setup.
The PACKMAN Setup screen is displayed. - Select the Lists tab.
- Choose Patient Types from the Type box.
Amfac modules include commonly used patient types. For example:
- Deceased
- Discharge patient
- Inpatient
- Outpatient
- Regular
- Weekend leave.
You can add new patient types, or change the existing ones. A descriptive name for each patient type is stored.
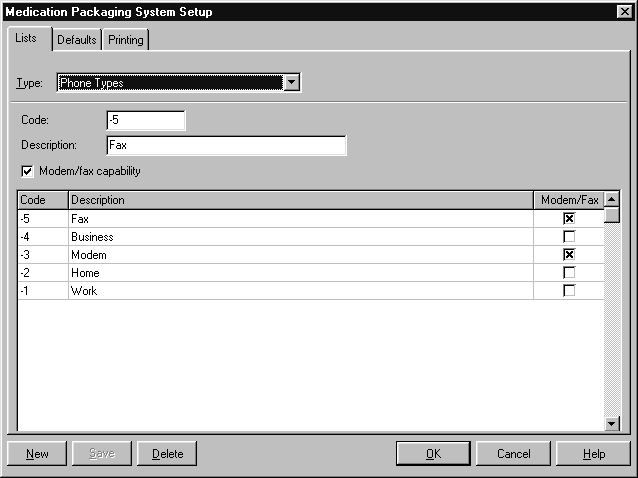
Phone Types #
Amfac modules include commonly used phone types such as:
- Fax
- Business
- Modem
- Home
- Work
To open the Phone Types list:
- From the Options menu, choose Module Setup.The PACKMAN Setup screen is displayed.
- Select the Lists tab.
- Choose Phone Types from the Type box.

To add a new phone type when entering a phone number in the work area, type its description into the box at the left of the phone number area.
The following information is stored about each phone type:
- Code
- Description
- Modem/fax capability
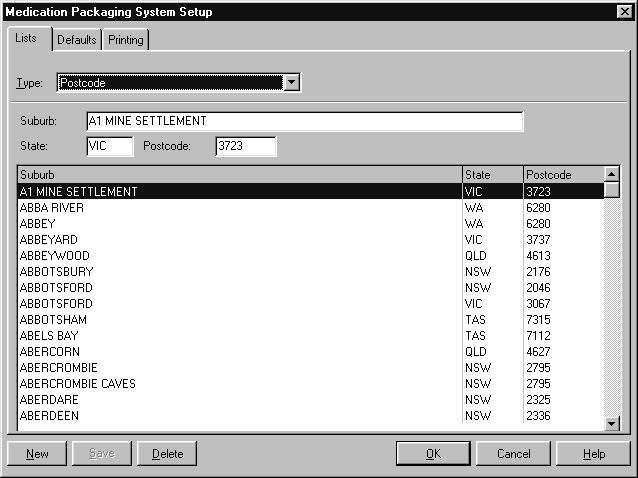
Postcodes #
Amfac modules are supplied with a comprehensive postcode guide covering all of Australia. These postcodes are available wherever addresses are used. For instance, on the Patient Details and the Doctors Details screens.
To open the Postcodes list:
- From the Options menu, choose Module Setup. The PACKMAN Setup screen is displayed.
- Select the Lists tab.
- Choose Postcodes from the Type box.
The following information is stored about each postcode:
- Suburb
- State
- Postcode
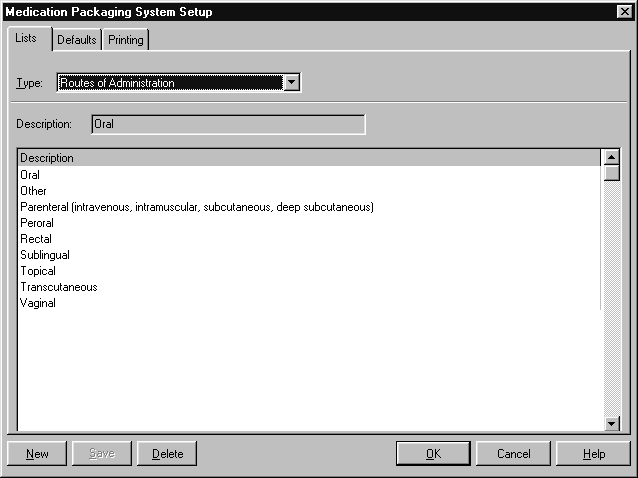
Routes of Administration #
Drugs can be prescribed by route of administration (e.g. penicillin oral) as well as form. Some aspects of medical checking also vary according to route. Amfac modules include a set of routes of administration.
To open the Routes of Administration list:
- From the Options menu, choose Module Setup. The PACKMAN Setup screen is displayed.
- Select the Lists tab.
- Choose Routes of Administration from the Type box.

You cannot add, edit or delete Routes of Administration provided with Amfac modules.
A description for each Route of Administration is stored.
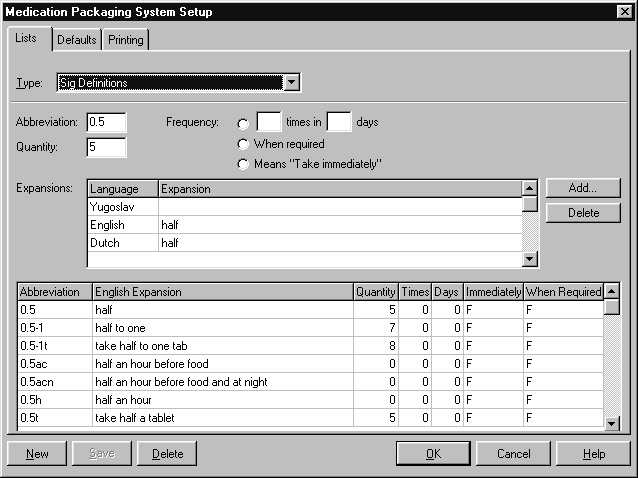
Sig Definitions #
Amfac modules include commonly used sigs. You can add new sigs, or change the existing ones.
To open the Sig Definition list:
- From the Options menu, choose Module Setup. The PACKMAN Setup screen is displayed.
- Select the Lists tab.
- Choose Sig Definitions from the Type box.
The following information is stored for each sig:
- Abbreviation
- Dosage checking interpretation information
- Expansions in various languages.
Abbreviation #
The abbreviation is the shortened form that you type instead of the full instructions. Amfac modules come with a set of common sigs.
When you are setting up your own sigs, type the abbreviation into the Abbreviation box. You can include a combination of letters, numbers and punctuation symbols. Do not use spaces.
Dosage checking interpretation information #
Healthlinks Dispensing checks each drug’s sigs against the recommended dosage for the medication as they are dispensed. To do this, dosage interpretation information is used.
The sigs provided with Amfac modules include dosage interpretation information. When you add your own sigs, you need to set this up if you want accurate dosage checking.
The following values need to be set:
- Quantity
- Frequency (i.e. dose frequency, when required, means immediately).
Quantity
To describe a single quantity:
- In the Quantity box, type the value to one decimal place.
To describe a range of quantities:
- In the Quantity box, type the preferred value.
Amfac sigs use the average value of the range.
For example:
The sig 1-2 expands to one to two. In this example, Quantity is set to 1.5.
Dose Frequency
Use the times in and days boxes to set dose frequency.
- In the times in box, type the number of times that the dose is to be administered.
- In the days box, type the number of days over which the dose applies.
For example:
The sig tds expands to three times a day. In this example, frequency is set to 3 times in 1 day.
When Required
If the sig means “when required,” select the When Required option. When this sig is used, dose frequency is ignored and only the dose quantity is displayed.
For example:
The sig prn, expands to when required.In this example, the When Required button is selected
Means Immediately
If the sig means “immediately,” select the Means Immediately button. When this sig is used, dosage checking is done on the sigs that are following.
For example:
The sig st expands to immediately. In this example, the Means Immediately button is selected.
The sig 2 st then 1 d cc expands to Take two tablets at once then one daily with food.
In this example, dosage checking is done on the then 1 d cc only.
Combining Sigs
You can use these in any combination to describe the meaning of the sig.
For example:
The sig vib expands to Take two at once, then one daily with food or milk. In this example, quantity is set to1.0 and frequency is set to 1 time in 1 day.




